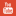
Psoriasis is a type of chronic autoimmune condition that causes a rapid increase in the cells of the skin. As a result of this increment in cells, there is scaling on the surface of the skin. The scaling of the skin leads to redness and inflammation of the scales, which is referred to as psoriasis. Frequent sightings include red patches on elbows, knees, and palms.
PsoriasisTypes
There are diverse psoriasis types that are segregated on the nature of the condition along with their location and intensity on the body:
- Pustular psoriasis: Prevalent among adults, pustular psoriasis causes blisters filled with pus and inflammation of the skin. Confined to small parts of the body, such as hands and feet, it can spread to other parts of the body as well.
- Guttate psoriasis: It occurs in children and causes pink spots on the skin. The common sites of this psoriasis include the arms, legs, and torso. The size of the spots becomes medium thick because of the inflammation.
- Plaque psoriasis: One of the most common types of psoriasis is plaque psoriasis. The majority of the patients who suffer through psoriasis are found to have plaque psoriasis. In this type, there is redness on the skin, and silver scales are formed. The plaques are located on the surface of the elbows, scalp, and knees.
- Inverse psoriasis: In inverse psoriasis, patches are formed under the breasts or around the skinfolds inside the genitals. The patches are red and produce shiny inflamed skin.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: In this type of psoriasis, the skin appears sunburnt, and scales get developed in the form of sheets. This condition is a rare case and could be life-threatening, if not given attention.
PsoriasisCauses and Triggers
Two factors lead to the occurrence of psoriasis causes in the human body. These two factors are the immune system and genetics.
- Overactive Immune System: In the autoimmune conditions, the white blood cells attack the skin cells. The defenders (WBC) become attackers. As a result, the immune system get weakens. Generally, the white blood cells destroy the invading foreign bacteria. However, in psoriasis, the WBC mistakenly increases skin cell production. The increase in piles up skin cells to form plaques. These plaques cause redness and inflammation on the skin surface.
- Genetics Some genetic reasons lead to the development of psoriasis in the human body. If a person has a family history of psoriasis, then he is likely to get the disease. Also, if a person’s immediate family member is suffering from any skin condition, then there are more chances of getting psoriasis.
Triggers for psoriasis aren’t similar for everyone and could change in time. They evoke the deep-seated condition at various points in time. Here are some of the most common factors that trigger the disease and even lead to flare-ups:
- Stress: Stressful conditions could trigger a flare-up of the disease
- Alcohol: A person with heavy alcohol use may also lead to psoriasis outbreaks, even boosting their frequency.
- Injury: An accident that included bruises, cuts, or scrapes could also lead to the condition. Beware of specific shots and vaccines that could cause a new flare-up.
- Medications: Some medications act as triggers, including lithium, blood pressure medicines, etc.
- Infection: The condition is caused when the immune system starts fighting the healthy skin cells. The disorder could mainly happen when stricken with infection when your immune system could go overboard.
Who are Prone to Psoriasis?
One could suffer from psoriasis at any age, but the average age of onset of the condition is 15 – 35 years. WHO studies reveal 75 percent of the cases happen before one turns 46 years old. Nearly one-third of those who have developed psoriasis are affected by psoriatic arthritis. People prone to psoriasis include those who are already suffering from
- Diabetes (Type 2)
- Kidney problems
- Heart ailments
- High blood pressure
Psoriasis Symptoms
The symptoms of psoriasis differ from person to person and also depend upon the psoriasis type. The most visible symptoms include
- Soreness around the patches
- Formation of silver scales on the red patches
- Bleeding in the dry skin
- Swollen and painful joints
The presence of the above symptoms comes in cycles in an individual. Sometimes the symptoms are at a peak, and sometimes they are unnoticeable. Therefore, it is advisable to take immediate medical attention.
Psoriasis Diet Recommendations and Foods to Avoid with Psoriasis
Here are some foods to avoid with Psoriasis and some diet recommendations to avoid the incidence of the condition:
- Lose weight: Try to lose weight to reduce the condition’s severity.
- Eat a diet that is good for the heart: Reduce saturated fats intake and increase intake of lean proteins inclusive of omega-3 fatty acids, derived from sardines, shrimp, walnuts, and soybeans.
- Avoid trigger foods: Avoid trigger foods such as red meat, refined sugar, dairy products, etc.
- Drink less alcohol: Cut back or leave drinking alcohol entirely
- Consider taking vitamins: A vitamin-rich diet may help you get adequate nutrients
Homeopathic treatment
In homeopathy, the root causes of the psoriasis are targeted. Homeopathy understands that psoriasis is due to the weak immune system of the body and, therefore, uses the natural remedies to resolve the same. The best doctor for Psoriasis can be a Homeopathic doctor who can use a specific homeopathic remedy to restore the body to a perfect, harmonious balance. A Psoriasis specialist can propose treatments considering the fact that skin eruptions like these are an external manifestation of a faulty immune system that is overdoing the elimination of threats away from all major organs. The skin needs adequate time to heal itself aided by the right homeopathic medicine for psoriasis.
The best medicine for psoriasis is to allow the body to heal naturally without suppressing the disorder from treating itself. By stimulating the immune system, the treatments improve the body from the root of the problem.